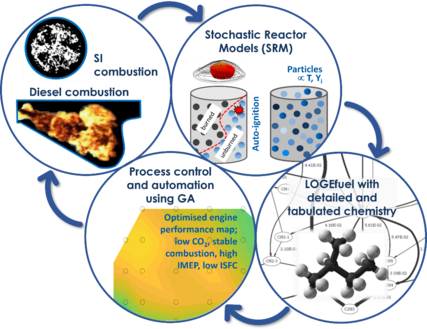
LOGEengine ES
LOGEengine ES is a simulation platform for designing and analysing combustion in internal combustion engines. It couples the Stochastic Reactor Model (SRM) of the engine in-cylinder process with LOGEfuel for detailed and tabulated reaction kinetics-based prediction of engine exhaust emissions formation, and optimisation algorithms for simulation process control and automation. Fast simulation times, combined with an intuitive GUI, make LOGEengine ES suitable for fast parameter studies and prototyping of the combustion process in internal combustion (IC) engines [Figure 1].
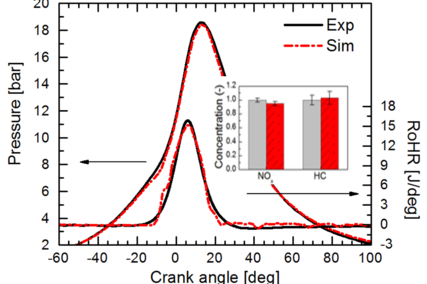
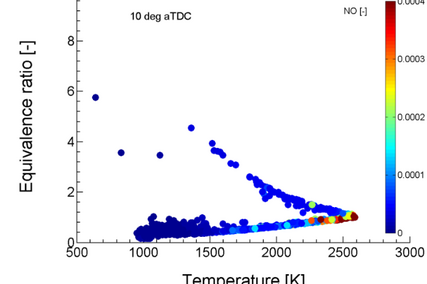
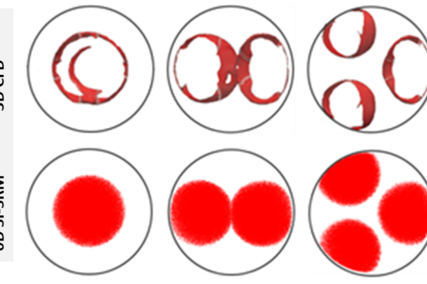
The simulation process with LOGEengine ES is an interplay between thermodynamics analysis of the measured engine in-cylinder pressure history and combustion analysis. The thermodynamics analysis determines initial conditions such as temperature or EGR. At the foundation of the combustion analysis lies the 0D SRM, which accounts for engine processes such as piston motion, fuel injection, chemistry, heat transfer, and flame propagation. The SRM considers gas inside the cylinder as an ensemble of notional particles. Each particle has chemical composition, temperature and mass representing a point in the gas phase. These scalars are treated as random variables and can vary within the cylinder. The particles can mix and exchange heat with the cylinder walls. The mixing between particles is stochastic and allows for the representation of inhomogeneity [Figure 2] of the in-cylinder mixture, which is particularly important when simulating emissions formation. Furthermore, cycle-to-cycle variation in spark ignition (SI) engines can be mimicked [Figure 3]
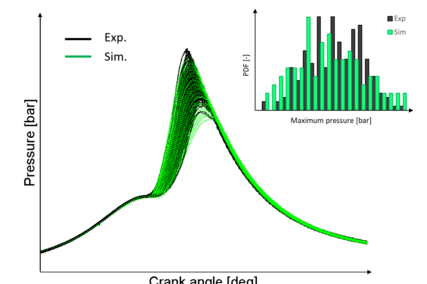
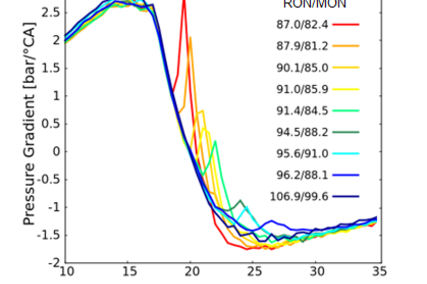
Thanks to detailed consideration of reaction kinetics, details of pollutant formation and fuel effects can be studied. Monte Carlo-based modelling of flame propagation [Figure 4] through the cylinder and distinguishing between burned and unburned zones with chemistry solved in each zone enables one to estimate the tendency to knocking combustion in SI engines [Figure 5]